This method has a good application prospect in the semiconductor lighting industry and even the entire semiconductor industry, but further experimental data is needed to provide support. The university's scholars believe that because diamond nanoparticles are produced under high temperature and high pressure conditions, carbon ions are always associated. Therefore, this synthesis method can be realized not only by silicon but also inside other substances. As early as three years ago, the university began to engage in carbon ion pulse testing, and obtained carbon implant patents in 2012, which was included in the "Russian 100 outstanding invention patents" promulgated by the Russian Intellectual Property Office.
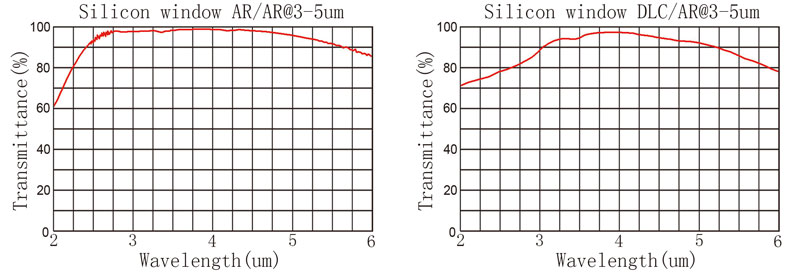
The refractive index of the monocrystalline silicon material is about 3.42, and the reflectivity of the silicon lens after polishing is about 30% in the air environment. Our common silicon lens and silicon window can be coated on the surface (Antireflection Coating), which can reduce the reflectivity to less than 1.5% between 3 to 5 um.
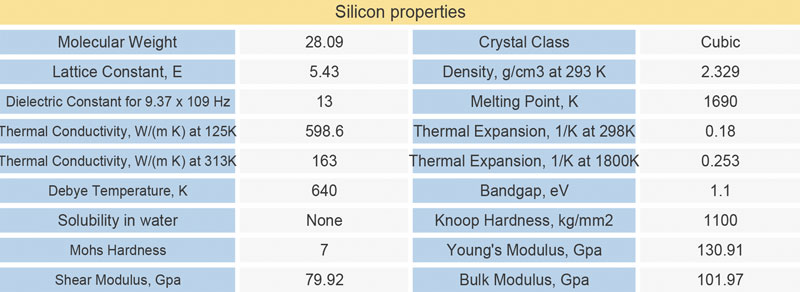
Some silicon elements, especially the silicon protected windows, are exposed to dust, acid, salt and so on in the harsh environment. The conventional multilayer antireflection coating will be damaged and affect the normal work of the equipment. At this time, we need to make DLC coating on the surface of the silicon lens.
Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) Coated Silicon Windows are engineered for 3 to 5µm, making them ideal for infrared defense applications such as thermal imaging.
Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) Coated Silicon Windows provide anti-reflection coating on one surface and a specially designed DLC coating on the other surface, making these windows highly durable and ideal for harsh environments.
| Silicon lens specifications: | ||
| Standard precision | High-precision | |
| Dimension Tolerance | φ5-250mm+0/-0.2 | φ3-350mm+0/-0.2 |
| Thickness Tolerance | 1-50mm+/-0.1 | 1-50mm |
| Centration | 3 arc minute | 1 arc minute |
| Surface Quality | 60/40 | 20/10 |
| Power(fringe@633nm) | N<λ/2@633nm(in 25mm) | N<λ/10@633nm(in 25mm) |
| Clear Aperture | >90% | >95% |
| Chamfer | Protected <0.5mmx45deg | Protected <0.5mmx45deg |
Silicon Lens,Silicon Optical Lens,Infrared Si Lens,Silicon Plano-Convex Lens
China Star Optics Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.realpoooptics.com